Streamline Your SAP Integration with Advanced Mapping Tool
SAP Mapping Tool is a robust solution tailored to streamline and optimize your SAP integration processes. The tool empowers users to assign mapping tables to interface types, ensuring that every data transaction is seamless and error-free.
With features like user-defined mapping tables and an intuitive interface, you can customize your integration processes to align with specific business needs. The tool also supports advanced functionality, such as executing reports that dynamically determine attribute values from predefined tables. If entries are missing or inconsistent, the system is equipped to handle exceptions gracefully, ensuring reliable and accurate outcomes.
By leveraging the SAP Mapping Tool, organizations can reduce manual errors, improve system interoperability, and enhance overall productivity. Whether you're managing GL accounts, document types, or source attributes, this tool provides the flexibility and precision you need to achieve seamless SAP integration and drive business success.
Step 1. Define Logical Systems
In this step, the logical systems used within the SAP environment are defined. A logical system represents an application system in a distributed environment, uniquely identified to enable smooth communication between different systems.
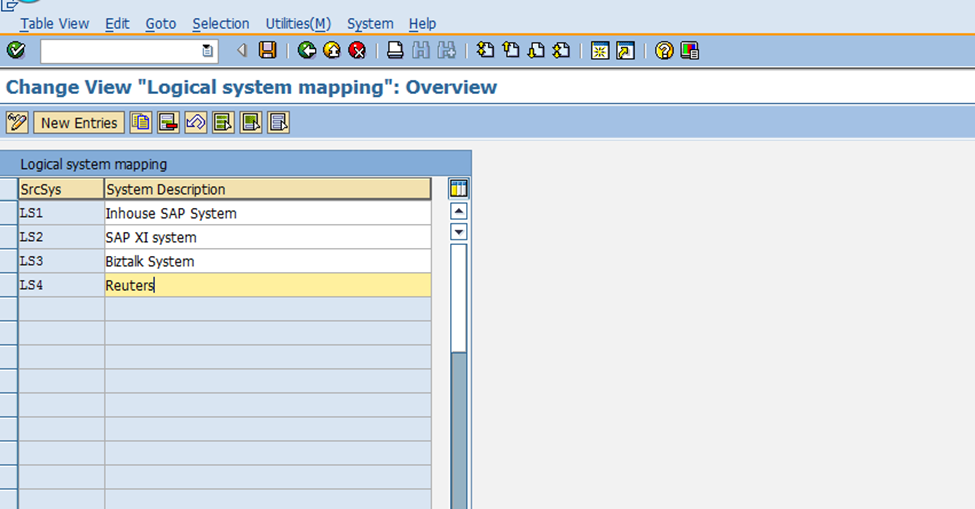
Step 2. Assign Logical Systems to partner profiles
In this step, the logical systems defined earlier are assigned to partner profiles. Partner profiles are essential for establishing communication and data exchange between systems in an SAP environment.
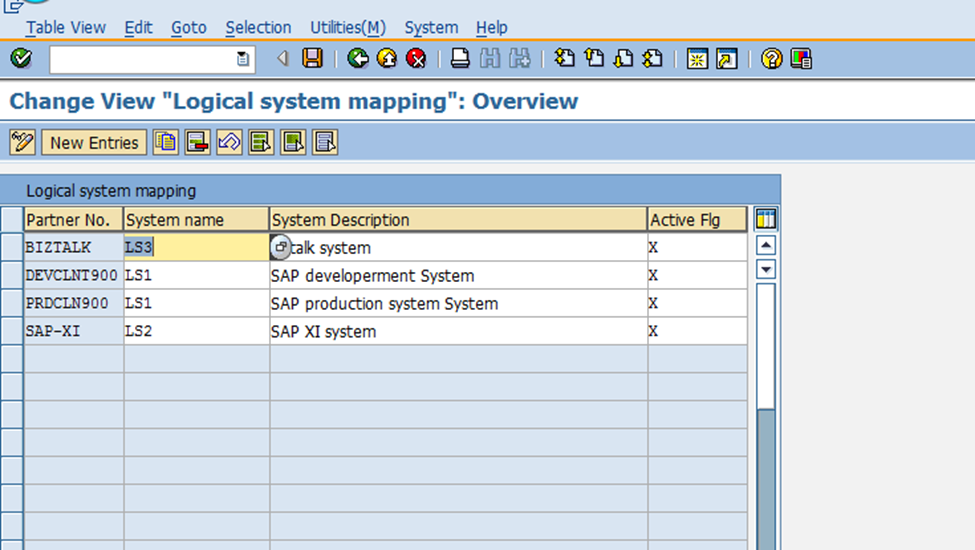
Step 3. Define Interface Attributes
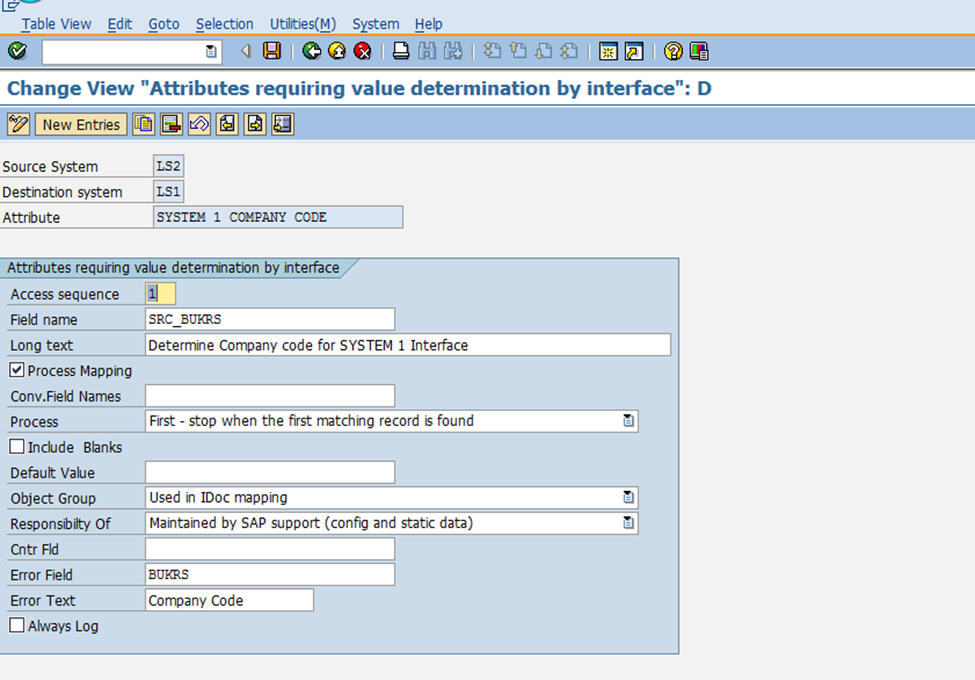
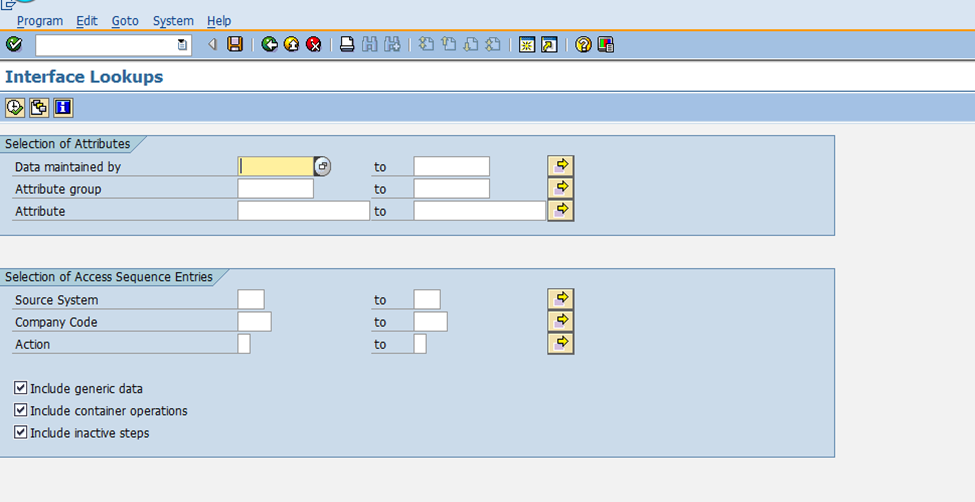
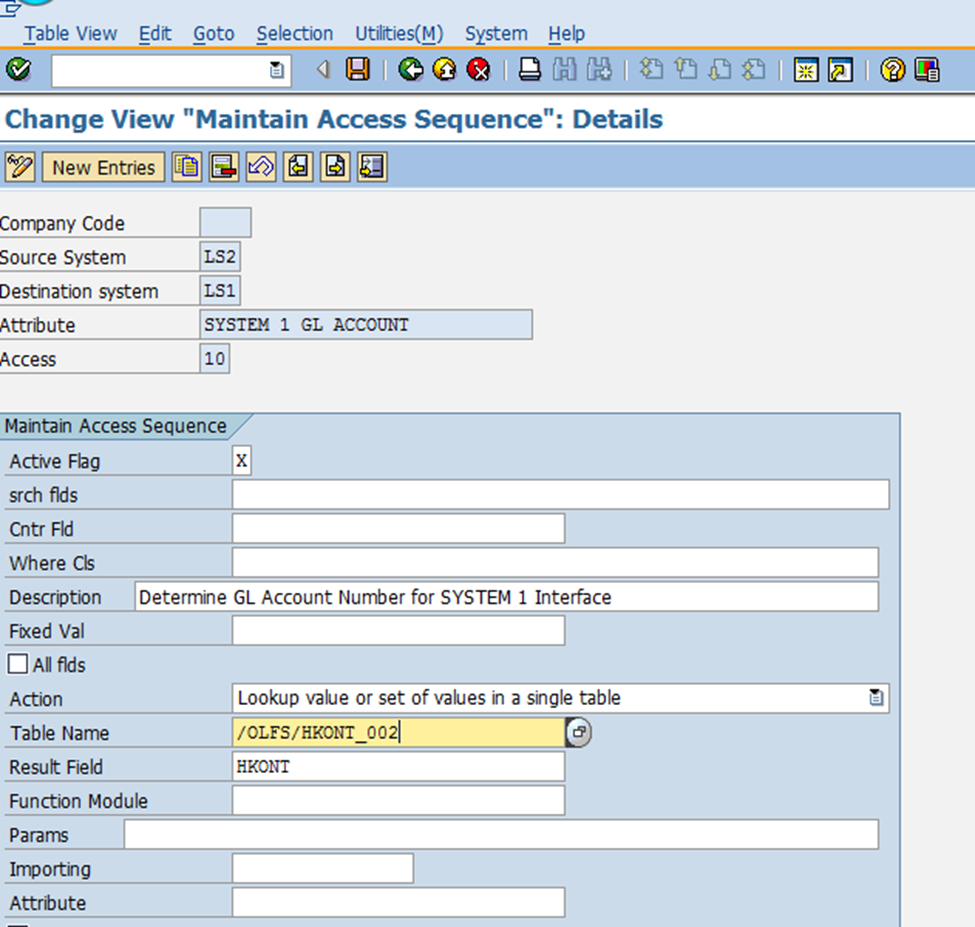
In this step, interface attributes are configured to enable accurate value determination and data mapping between source and destination systems. The purpose of this step is to define the specific parameters, rules, and processing logic that govern the exchange of data in an integration scenario.
Key Configuration Fields in the Screenshot:
- Source System: Specifies the originating system (e.g., LS2 in this example).
- Destination System: Identifies the receiving system (e.g., LS1 in this example).
- Attribute: Defines the context or purpose of the mapping (e.g., "SYSTEM 1 COMPANY CODE").
- Access Sequence: Determines the order in which the mapping logic or conditions are applied.
- Field Name: Specifies the field to be mapped or processed (e.g., SRC_BUKRS for company code).
- Process Mapping: Indicates that process mapping logic is enabled.
- Long Text: Provides a description of the mapping logic (e.g., "Determine Company Code for SYSTEM 1 Interface").
- Process Logic: Specifies how the data is handled (e.g., "First - stop when the first matching record is found").
- Error Field and Error Text: Identifies the field and corresponding error message if mapping fails (e.g., BUKRS with error text "Company Code").
- Object Group and Responsibility: Defines the context (e.g., "Used in IDoc mapping") and ownership (e.g., "Maintained by SAP support").
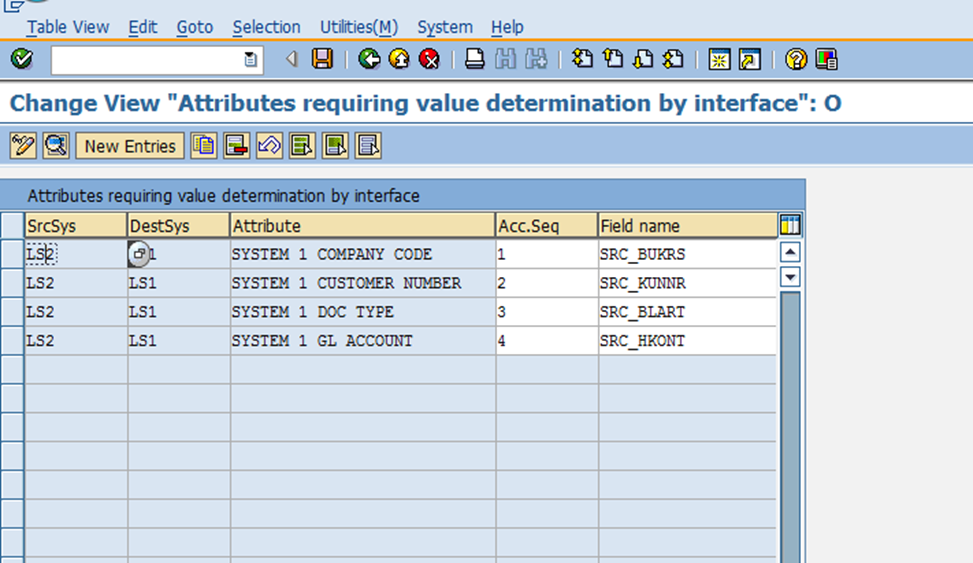
Step 4. Assign mapping tables to Interface Types
In this step, mapping tables are linked to specific interface types to facilitate seamless data transformation between systems. Mapping tables play a critical role in ensuring that the attributes of source systems are accurately mapped to corresponding attributes in the destination systems.
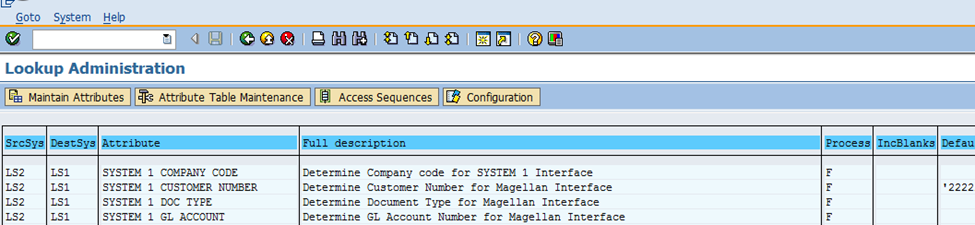
Step 5. User Defined Mapping table
In this step, user-defined mapping tables are created and configured to manage specific mapping requirements for integration scenarios. These mapping tables provide a flexible way to handle custom data mappings, such as GL Accounts or document types, between source and destination systems.


Step 6. Use mapping functionality in your program
The provided ABAP program demonstrates how to call a mapping function module `/OLFS/DET_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE` to dynamically determine a mapped value based on predefined mapping tables. Below is an explanation of its structure and purpose:
Key Components:
-
1. Input Parameters:
p_SOURCE: Source system identifier (e.g., 'LV2').P_DEST: Destination system identifier (e.g., 'LV1').lv_attr: The attribute name to determine (e.g., 'SYSTEM 1 GL ACCOUNT').
-
2. Container Data Structure:
lt_container: Table used to hold input mapping elements (key-value pairs).wa_container: Work area to define mapping elements such as SRC_BUKRS (company code), SRC_BLART (document type), and SRC_HKONT (GL Account).
-
3. Mapping Function Module Call:
- The program uses the function module
/OLFS/DET_ATTRIBUTE_VALUEto determine the mapped value based on: - Source system (
p_SOURCE) - Destination system (
P_DEST) - Attribute (
lv_attr) - Key-value pairs stored in
lt_container
- The program uses the function module
-
4. Key Fields and Mapping Rules:
- Each key-value pair represents a mapping parameter:
SRC_BUKRS: Company code (e.g., '1212')SRC_BLART: Document type (e.g., 'ZA')SRC_HKONT: GL Account (e.g., '9999999990')
-
5. Returned Values:
lv_map_value: The determined mapped value (e.g., a GL Account)lv_table: The last mapping table accessed to determine the value
-
6. Error Handling:
- If the function module fails (
SY-SUBRC <> 0), an appropriate error message is displayed using the system message variables.
- If the function module fails (
